Approximate Bayesian Methods for Hodgkin-Huxley Model and its Bifurcation Analysis
Investigates the dynamics and bifurcations of the Hodgkin-Huxley model
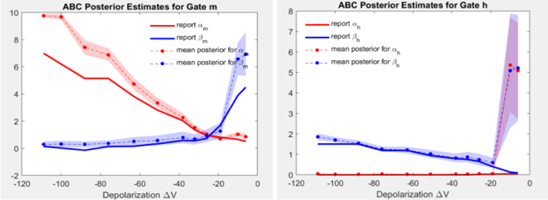
This research investigates the dynamics and bifurcations of the Hodgkin-Huxley model, a foundational model in neuroscience, through both classical analysis and modern computational techniques. The Hodgkin-Huxley model describes the action potentials of neurons and serves as a cornerstone in understanding neural communication. While traditional methods have provided deep insights into the model’s behavior, recent advancements in reparameterization using Approximate Bayesian Computation (ABC) offer new perspectives on parameter estimation and uncertainty quantification. This study applies ABC methods to the Hodgkin-Huxley model to infer posterior distributions of critical parameters, addressing challenges posed by the complexity and high-dimensional nature of the model. Through ABC rejection sampling and more sophisticated Sequential Monte Carlo (SMC) approaches, the research demonstrates improvements in fitting accuracy compared to classical techniques. These methods open pathways for further exploration of the model’s parameter space and can be extended to more complex neural models, providing a robust framework for bridging mechanistic models and data-driven approaches in neuroscience.