Modelling of Electrical Activity of Cardiac Tissue using 2D Poisson's Equation via Finite Element Method
Modeling the electrical activity of cardiac tissue using the 2D Poisson’s equation
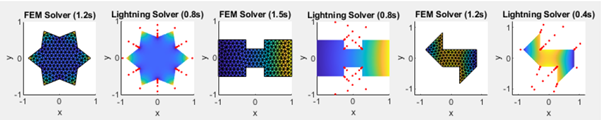
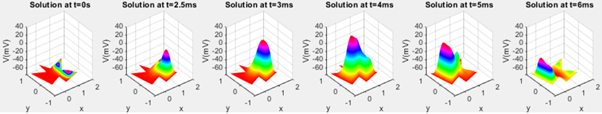
In this study, we model the electrical activity of cardiac tissue using the 2D Poisson’s equation, solved via the Finite Element Method (FEM). The Poisson equation is critical for understanding the behavior of electrical potentials across cardiac tissue, especially in simulating conditions like ventricular fibrillation and the heart’s response to defibrillation. We extend the analysis by integrating the monodomain model, which couples the 2D Poisson’s equation with the Hodgkin-Huxley model, providing a detailed framework for simulating the electrical signals in cardiac cells. This approach not only allows for a comprehensive simulation of heart tissue’s electrical activity but also highlights the FEM’s flexibility and efficiency in tackling complex biomedical problems. Through numerical experiments, we validate the FEM solver, comparing it with alternative methods and discussing the implications of our results for cardiac electrophysiology simulations. The study concludes with recommendations for improving the accuracy of the FEM model, particularly in handling irregular domains and mixed boundary conditions.